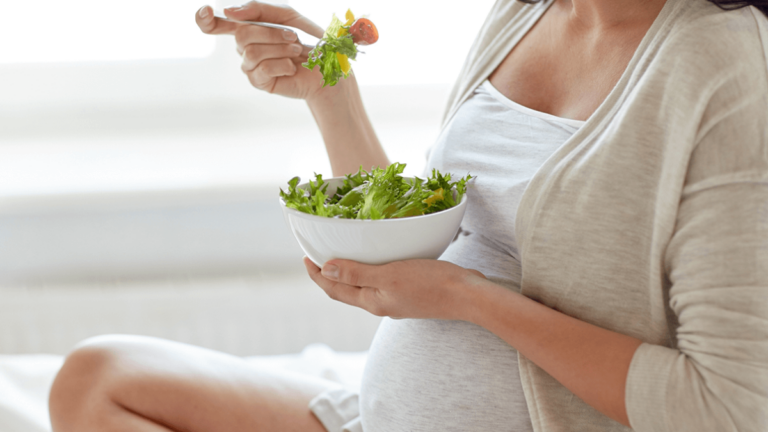
Pregnancy marks a time of extraordinary growth and change, and amid this transformation, protein emerges as a vital nutrient. Often referred to as the body’s “building blocks,” protein plays a central role in supporting the development of your baby’s cells, tissues, and organs, while maintaining your own well-being. This article delves into the significance of protein during pregnancy and explores diverse sources to meet your protein requirements.
Understanding Protein’s Significance:
Protein is a cornerstone nutrient during pregnancy. Your body demands additional protein to aid in building the placenta, amniotic fluid, and your baby’s organs and tissues. It’s also pivotal for producing red blood cells that transport oxygen to both you and your baby.
Determining Your Protein Needs:
As a general rule, aiming for an extra 25 grams of protein daily compared to your pre-pregnancy intake is advised. Yet, individual needs may fluctuate based on factors like your pre-pregnancy weight, activity level, and overall health. For personalized guidance, consulting a healthcare provider or registered dietitian is recommended.
Abundant Protein Sources During Pregnancy:
- Lean Meats and Poultry: Opt for lean cuts that supply ample protein without excess saturated fats. Skinless chicken, turkey, and lean beef or pork are excellent choices.
- Fish: Fatty fish, such as salmon and sardines, not only provide protein but also furnish essential omega-3 fatty acids crucial for your baby’s brain and eye development.
- Eggs: Versatile and packed with protein, eggs are also a source of choline—a nutrient essential for brain development.
- Dairy and Dairy Alternatives: Greek yogurt, cottage cheese, and fortified plant-based milks deliver protein alongside bone-strengthening calcium.
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, chickpeas, and peas offer plant-based protein, coupled with fiber, iron, and folate—beneficial nutrients during pregnancy.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, chia seeds, and pumpkin seeds supply not only protein but also healthy fats, vitamins, and minerals.
- Tofu and Tempeh: These soy-based options provide a meatless protein alternative that adapts well to a range of dishes.
- Whole Grains: Quinoa, brown rice, and whole wheat pasta contribute protein alongside complex carbohydrates, sustaining your energy levels.
Achieving Protein Balance:
Aim for dietary equilibrium by incorporating a mix of protein sources. Merging plant-based and animal-based proteins ensures a comprehensive array of essential amino acids. Remember that the quality of protein matters as much as the quantity—focus on nutrient-rich, lean selections.
In Closing:
As you embrace this incredible journey of pregnancy, acknowledge the indispensable role protein plays in nourishing both you and your baby. Rely on a diverse range of protein sources to cater to your evolving nutritional needs. Guidance from a healthcare provider or registered dietitian empowers you to make well-informed choices, supporting a thriving and healthy pregnancy